Exchange
Exchange is the one of core contracts that serves the mechanics around the tokens.
Overview of Exchange Functionality:
This contract enables the exchange of tokens in a flexible manner, with various exchange mechanics available such as * *Claim**, Grade, Purchase, etc. This functionality allows users to exchange one or multiple assets. However, to prevent unauthorized transactions, a trusted source (Server) must sign the transaction before it can be executed on the blockchain. Once the signature and additional information from the Server response are obtained, they can be combined with the Asset information to execute the exchange on the blockchain.
Workflow of Purchase mechanics.
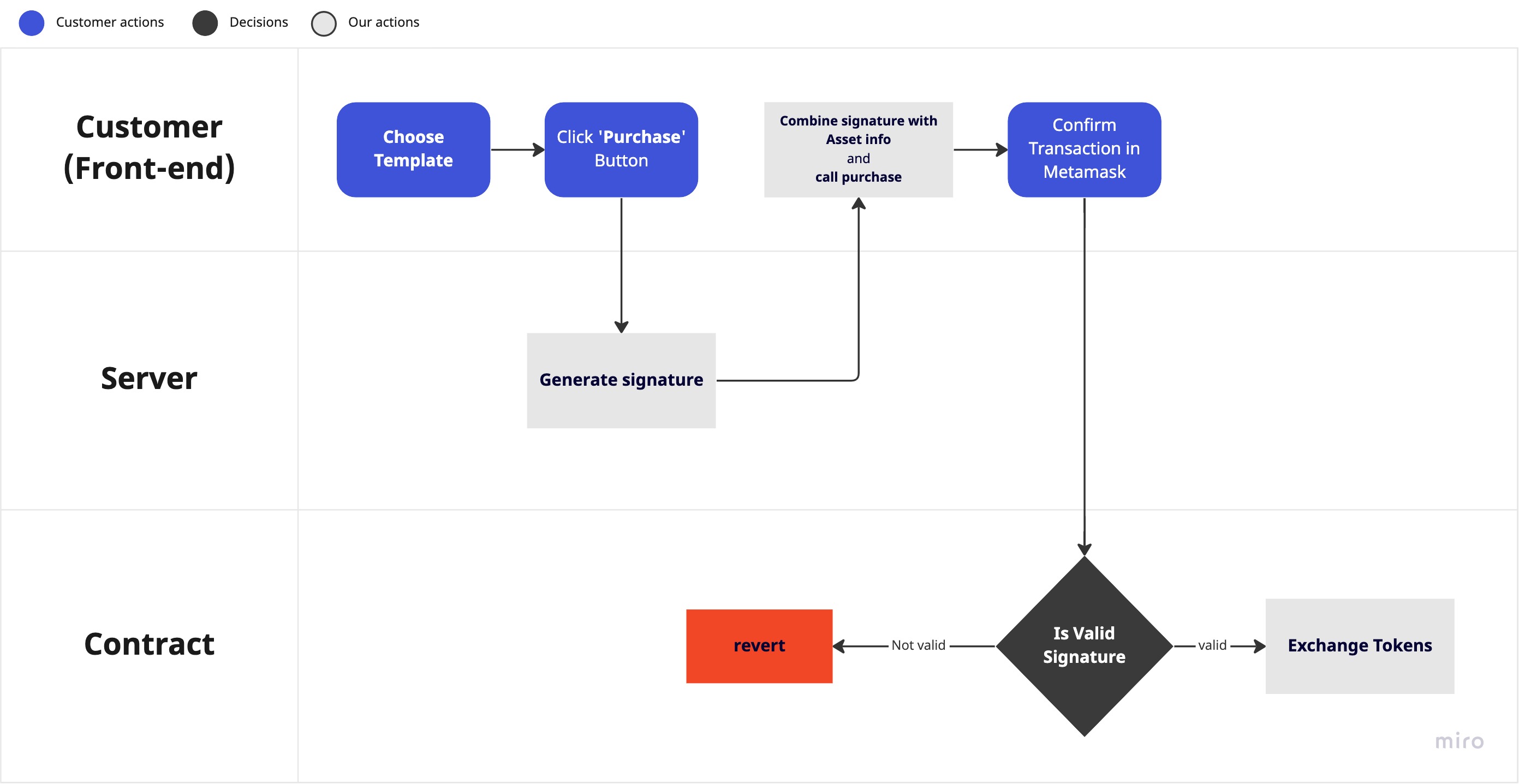
Signing a Purchase Transaction:
To sign any transaction, we use the standard EIP-712. This combines all parameters passed to the contract function into one string and hashes them. When executing the transaction, the address will be recovered from signature and contract will check this address for the appropriate minting rights. If the address has the necessary rights, the transaction is processed.
To sign a transaction via the Server endpoint, several arguments must be provided, including the account address, the referral address (if not applicable, pass '0x'), and the templateId.
Different mechanics mey require different input. For Excample Craft require only craftId.
The response will be similar to this:
{
nonce: "0x1c37fa85c31c5fa39dc...",
signature: "0x1c5fa85c31c5fa39dc1c5fa85c31c5fa39dc...",
expiresAt: 0
}
Executing Purchase on Blockchain:
Whenever a signature is available, the purchase can be executed on the blockchain.
First of all need to check - ExchangeContract have allowance for all tokens in price. If not we have to approve tokens.
Second we have call function that will perform the purchase. In order to create an instance of the ExchangeContract we need address and ABI of ExchangeContract.
All contracts in our ecosystem use the same logic for exchange and have almost the same arguments for executing:
- params:
- nonce : Unique request ID,
- externalId : This is the ID in the database that applies to the specific mechanic. In the case of Purchase, the externalId would be equal to the templateId of the template being purchased. For Craft, the externalId would be equal to the craftId of the crafting recipe being used.
- expiresAt : This parameter describes how long signature would be valid (If equal to 0, don't have any time limitations),
- referrer : This is the address of the person who invited the account to the platform. If a referral program is not installed, the value '0x' should be passed as the referrer. The referrer is used to track referrals and reward the person who made the referral.
- item: Asset that user will receive,
- price: Assets that user must transfer,
- sign: This is a hash of all the arguments listed above but is was generated on the server and must contain the same parameters as listed above, with the exception of signature itself. The signature ensures the authenticity of the transaction and prevents tampering or modification of the transaction data during transmission.
Some notes:
If Native tokens are in the "price", the transaction must be executed with the same value as a sum of all price.amount.
If the Exchange functionality (Purchase, Grade, etc.) accepts an array of "item" or "price", multiple assets can be passed for transfer or received as long as there is enough gas in the transaction.
The arguments for signing a transaction and executing an exchange must be exactly the same (params, item, price). The exchange function on contract requires a combination of the signature response params and asset information (item, price). For signing a transaction, only a few properties (account, referrer, templateId) are required. The server collects the rest of the exchange information (item, price) and signs it. This is done to prevent user manipulation of signature inputs from the front-end and ensure server control of all signatures for security reason.